 This is a brief video on congenital disorders affecting biological gender, the genitalia, and reproductive health.
This is a brief video on congenital disorders affecting biological gender, the genitalia, and reproductive health.
I created this presentation with Google Slides.
Image were created or taken from Wikimedia Commons
I created this video with the YouTube Video Editor.
ADDITIONAL TAGS:
Disorders of
sexual development
Congenital disorders affecting traits of gender, the genitalia, and reproductive health
McCune-Albright syndrome
Turner’s
syndrome
Klinefelter syndrome
Androgen insensitivity syndrome
5 alpha
reductase deficiency
Kallmann
syndrome
McCune-Albright syndrome
Genetic disorder causing precocious puberty
Pathophysiology: defect in G3 alpha subunit protein makes it constitutively active
Chimeric, so several/various tissues affected
Gonadotropin-independent
Clinical: early breast development, early puberty
Hyperthyroidism, hyperparathyroidism, café-au-lait spots with “coast of Maine†borders
Treat with aromatase inhibitors to limit estrogen
Genetic disorder of delayed puberty and no periods (primary amenorrhea)
Result of ovarian failure; streak gonads
PE: short stature; shield chest with widely spaced nipples; webbed neck; and prepubertal vagina, uterus, and cervix
Lab tests: high FSH, high LH, low estradiol
Karyotype: 45 XO
Associated: renal problems, autoimmune (Hashimoto's thyroiditis), cardiac (aortic coarctation, aortic aneurysm, mitral valve prolapse, bicuspid aortic valve)
Treatment: growth hormone, hormone replacement, egg donation for childbirth (with significant risks)
Neck webbing
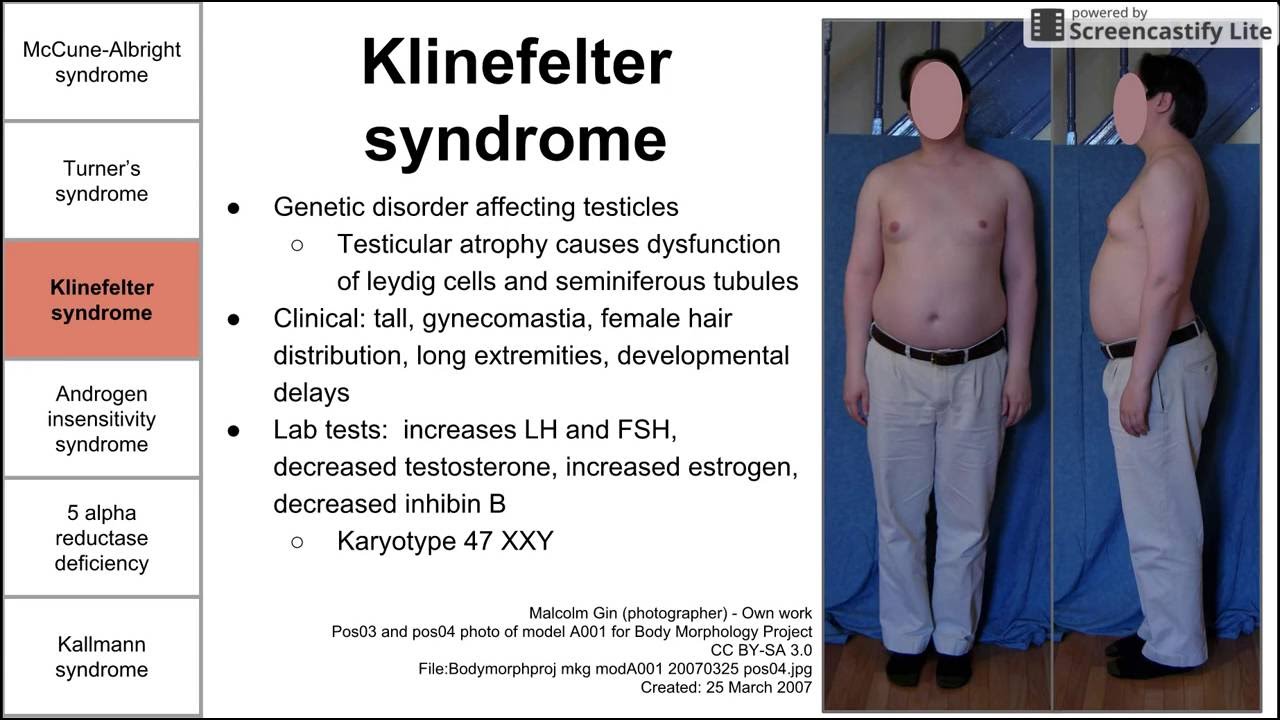
Genetic disorder affecting testicles
Testicular atrophy causes dysfunction of leydig cells and seminiferous tubules
Clinical: tall, gynecomastia, female hair distribution, long extremities, developmental delays
Lab tests: increases LH and FSH, decreased testosterone, increased estrogen, decreased inhibin B
Karyotype 47 XXY
Androgen insensitivity syndrome
AKA testicular feminization
Caused by inactivating mutation in androgen receptor gene in end organs
Male genotype, female phenotype, appears normal until pubertal age when menstruation doesn’t happen
Short vagina with little sexual hair; no cervix, no uterus bc testes produce anti mullerian hormone during development
Lab tests: FSH normal, LH normal, estrogen normal, LH:FSH is high, testosterone very high
Treat with HRT, testes removal (usually in labia majora), expansion of vagina
5 alpha reductase deficiency
5 alpha reductase converts testosterone to dihydrotestosterone
Genetic disorder, affects genetic males
Internal genitalia are male; ambiguous external genitalia until puberty, when increase in testosterone causes sudden testicular enlargement, phallus/clitorus enlargement, deepening of voice, increased muscle mass
“Penis at 12†syndrome
Lab tests: high testosterone, high testo/DHT ratio, 46 XY karyotype
Caused by “impaired migration of neurons†due to disorder in adhesion protein anosmin-1
Impaired migration of GnRH secreting neurons in the hypothalamus
Impaired migration of olfactory neurons → anosmia
Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism
Clinical: delayed puberty, anosmia, amenorrhea/low sperm count
Lab tests: low GnRH, low FSH, low LH, low estrogen
Treat with HRT for most symptoms; treat with recombinant FSH for fertility
By Neil Smith - Created ny a medical illustrator for the production of a booklet on Kallmann syndrome, CC BY-SA 3.0, https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?...
McCune-Albright syndrome
Turner’s
syndrome
Klinefelter syndrome
Androgen insensitivity syndrome
5 alpha
reductase deficiency
Kallmann
syndrome
Disorders of sexual development camera iphone 8 plus apk | |
| 196 Likes | 196 Dislikes |
| 21,816 views views | 26.7K followers |
| Education | Upload TimePublished on 26 Sep 2016 |
Không có nhận xét nào:
Đăng nhận xét